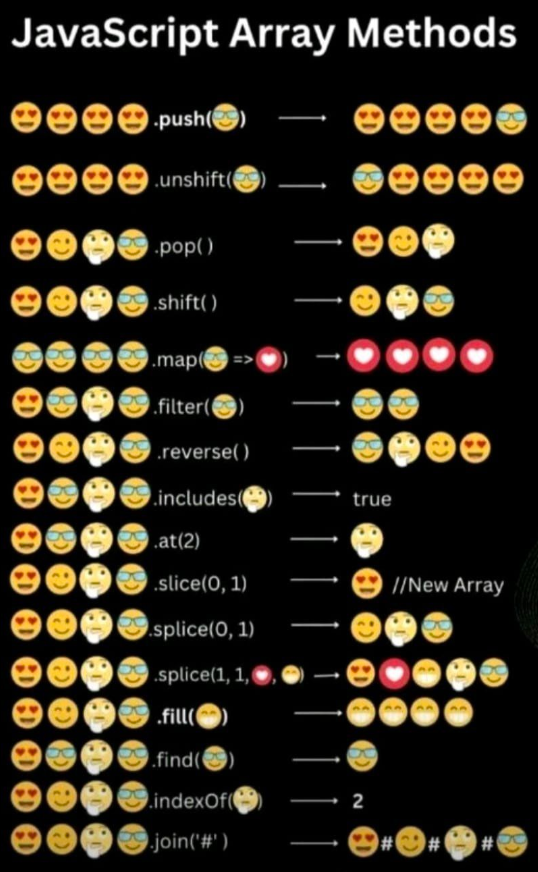
/
Gists
/
JavaScript
Gists - JavaScript
On gists
JavaScript
Optimize Complex Conditionals in JavaScript
index.js #
// https://blog.stackademic.com/how-to-optimize-complex-conditionals-in-javascript-0fcaf0add82a
const onButtonClick = (status) => {
if (status == 1) {
jumpTo('Index Page');
} else if (status == 2 || status == 3) {
jumpTo('Failure Page');
} else if (status == 4) {
jumpTo('Success Page');
} else if (status == 5) {
jumpTo('Cancel Page');
} else {
jumpTo('Other Actions');
}
};
// 1
// if => switch
const onButtonClick = (status) => {
switch (status) {
case 1:
jumpTo('Index Page');
break;
case 2:
case 3:
jumpTo('Failure Page');
break;
case 4:
jumpTo('Success Page');
break;
case 5:
jumpTo('Cancel Page');
break;
default:
jumpTo('Other Actions');
}
};
// ------------------------------------------
const onButtonClick = (status, identity) => {
if (identity == 'guest') {
if (status == 1) {
// logic for guest status 1
} else if (status == 2) {
// logic for guest status 2
}
// Additional logic for other statuses...
} else if (identity == 'master') {
if (status == 1) {
// logic for master status 1
}
// Additional logic for other statuses...
}
};
// 2
// interesting solution ;)
// nested if to map with keys where key mean concaten ifs..
const actions = new Map([
['guest_1', () => { /* logic for guest status 1 */ }],
['guest_2', () => { /* logic for guest status 2 */ }],
['master_1', () => { /* logic for master status 1 */ }],
['master_2', () => { /* logic for master status 2 */ }],
['default', () => { /* default logic */ }],
]);
const onButtonClick = (identity, status) => {
const action = actions.get(`${identity}_${status}`) || actions.get('default');
action();
};
// 3
// object with keys instead of use of ifs
const actions = {
'1': 'Index Page',
'2': 'Failure Page',
'3': 'Failure Page',
'4': 'Success Page',
'5': 'Cancel Page',
'default': 'Other Actions',
};
const onButtonClick = (status) => {
const action = actions[status] || actions['default'];
jumpTo(action);
};
On gists
Promise / Promise.withResolvers
•
JavaScript
example.js #
const { promise, resolve, reject } = Promise.withResolvers();
setTimeout(() => resolve('Done!'), 1000);
promise.then(console.log); // 'Done!'
function foo()
{
const {promise, resolve, reject} = Promise.withResolvers()
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('DONE')
}, 2000)
return promise
}
function foo2()
{
const {promise, resolve, reject} = withResolvers()
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('DONE 2')
}, 2500)
return promise
}
// polyfill
function withResolvers() {
let resolve, reject;
const promise = new Promise((res, rej) => {
resolve = res;
reject = rej;
});
return { promise, resolve, reject };
}
// Použití:
const { promise: aliasOnlyForTesting, resolve } = withResolvers();
(async() => {
const data = await foo()
console.log(data)
const data2 = await foo2()
console.log(data2)
})()
On gists
JavaScript
Lazy loading with IntersectionObserver
image-lazy-loading.js #
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
let lazyImages = document.querySelectorAll('.lazyload');
let observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
entries.forEach(entry => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
let img = entry.target;
img.src = img.dataset.src;
observer.unobserve(img);
}
});
});
lazyImages.forEach(img => {
observer.observe(img);
});
});
On gists
JavaScript
All datatypes in JS for testing
datatypes.js #
// Copied from https://javascript.plainenglish.io/structuredclone-the-easiest-way-to-deep-clone-objects-in-javascript-c503b536266b
const testData = {
number: 123,
string: "test",
undefined: undefined,
null: null,
boolean: true,
object: { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } },
array: [1, 2, { d: 3 }],
function: function() { return "hello"; },
map: new Map([["key1", "value1"], ["key2", "value2"]]),
set: new Set([1, 2, 3]),
date: new Date(),
error: new Error("An error occurred"),
regex: /test/i,
domNode: document.createElement("div")
}
On gists
JavaScript
Enum - JS
enum.js #
enum Direction {
Up,
Down,
Left,
Right
}
const Colors = Object.freeze({
RED: Symbol("red"),
BLUE: Symbol("blue"),
GREEN: Symbol("green")
});
/**
* Enum for common colors.
* @readonly
* @enum {{name: string, hex: string}}
*/
const Colors = Object.freeze({
RED: { name: "red", hex: "#f00" },
BLUE: { name: "blue", hex: "#00f" },
GREEN: { name: "green", hex: "#0f0" }
});
function createEnum(values) {
const enumObject = {};
for (const val of values) {
enumObject[val] = val;
}
return Object.freeze(enumObject);
}
// { Up: 'Up', Down: 'Down', Left: 'Left', Right: 'Right' }
createEnum(['Up', 'Down', 'Left', 'Right']);
class Direction {
static Up = new Direction('Up');
static Down = new Direction('Down');
static Left = new Direction('Left');
static Right = new Direction('Right');
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
toString() {
return `Direction.${this.name}`;
}
}
On gists
JavaScript
Toggle fn - closure in closure (fn returns fn)
toggle.js #
const toggle = (...list) =>
{
// To track the cycle.
let current = -1;
const length = list.length;
return function ()
{
// Increment current and used modulo to cycle back to the start.
current = (current + 1) % length;
// Returing the current element.
return list[current];
};
};
const toggleFunction = toggle("ON","OF");
console.log(toggleFunction()); // Prints "ON"
console.log(toggleFunction()); // Prints "OF"
console.log(toggleFunction()); // Prints "ON"
On gists
JavaScript
StructuredClone + set of all datatypes (@fatfish)
copy.js #
// https://javascript.plainenglish.io/structuredclone-the-easiest-way-to-deep-clone-objects-in-javascript-c503b536266b
const testData = {
number: 123,
string: "test",
undefined: undefined,
null: null,
boolean: true,
object: { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } },
array: [1, 2, { d: 3 }],
// function: function() { return "hello"; },
map: new Map([["key1", "value1"], ["key2", "value2"]]),
set: new Set([1, 2, 3]),
date: new Date(),
error: new Error("An error occurred"),
regex: /test/i,
// domNode: document.createElement("div")
}
const structuredCloneResult = structuredClone(testData)
console.log(structuredCloneResult)
/*
{
number: 123,
string: "test",
undefined: undefined,
null: null,
boolean: true,
object: { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } },
array: [1, 2, { d: 3 }],
function: undefined, // Functions are not cloned
map: Map { 'key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2' },
set: Set { 1, 2, 3 },
date: 2023-05-23T09:00:00.000Z,
error: Error: An error occurred,
regex: /test/i,
domNode: undefined // DOM nodes are not cloned
}
*/
On gists
JavaScript
Javascript function is object
fn.js #
/*
function in javascript is object and we can store what ever inside
*/
function x()
{
console.log('im x')
}
x.$version = '1.3.21'
x.callback = () => { console.log('what ever')}
console.log(x.$version);
x.callback();
On gists
Baby wolf codes - advanced JS tips
•
Popular ⭐
JavaScript
tips.js #
// Destructure into multiple variables
const obj = { val: 1 };
const { val: a, val: b, val } = obj;
console.log(a); // -> 1
console.log(b); // -> 1
console.log(val); // ->
// Chaining catch in Promise
const somePromise = async () => Promise.reject('error');
somePromise()
.then(e => {
//
})
.catch(e => {
throw new Error('error happened');
})
.catch(e => {
console.log('hi ' + e); // hi Error
});
// Multiple handlers for Promise
async function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
const promise = add(1, 2);
promise.then(e => `Result 1: ${e}`);
promise.then(e => `Result 2: ${e}`);
// -> Result 1: 3
// -> Result 2: 3
// Mixed promise handler liky try catch
async function someFunction() {
const res = await somePromise().catch(err => {
/* handle */
});
}
// Advanced default params
function test({ val = -1 } = {}) {
console.log(val);
}
test(); // -> -1
test({}); // -> -1
test({ val: 123 }); // -> 12
// Generate compact numbers
const formatter = Intl.NumberFormat('en',{ notation: 'compact' });
formatter.format('123'); // -> 123
formatter.format('1234'); // -> 1.2K
formatter.format('1235678'); // -> 1.2M
formatter.format('1235678901'); // -> 1.2B
//Default parameters previously declared
function test(x, y, z = x + y) {
console.log(z);
}
test(1, 1, 1); // -> 1
test(1, 1); // -> 2
// Additional arguments to setTimeout()
function callback(value) {
console.log(value);
}
setTimeout(callback, 1000, 5);
// -> Prints '5' after 1 second
// matchMedia
const query = window.matchMedia('(max-width: 600px)');
console.log('init -> ' + +query.matches)
query.addEventListener('change', event => {
console.log('change -> ' + +query.matches)
})
// promises
async function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function addAndDouble(a, b) {
return add(a, b).then(res => res * 2);
}
addAndDouble(1, 2).then(res => {
console.log(res); // -> 6
})